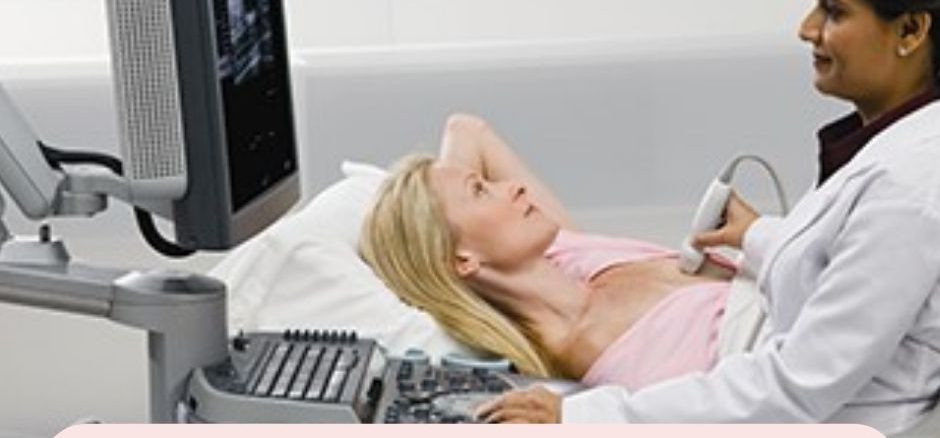
What is a breast biopsy?
A breast biopsy is a medical procedure in which a sample of breast tissue is taken for examination under a microscope. It can be taken with a special biopsy needle for a breast biopsy. Or it can be taken during surgery. It is usually done when a lump or abnormality is found during a physical examination, mammogram, or other imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI.
Types of biopsies taken from the breast are the following:
Core needle biopsy.
Fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy.
Open (surgical) biopsy.
Vacuum-assisted core biopsy.
Core needle biopsy:
A core needle biopsy is a non-surgical medical procedure that is used to obtain a sample of tissue from a suspicious area of the breast. During the procedure, a hollow needle is inserted into the breast tissue to remove small cylindrical samples of tissue from the targeted area. This method allows for a more accurate diagnosis compared to other biopsy techniques, as it provides larger tissue samples for examination. It is used to check for breast lumps or abnormalities found on imaging tests such as mammograms or ultrasounds. A pathologist analyzes tissue obtained from a core needle biopsy to determine if the cells are cancerous or benign, helping to guide further treatment decisions.
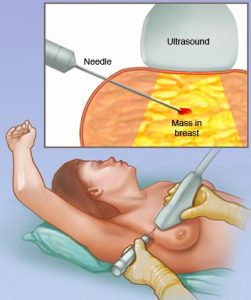
Fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy:
A fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy is a diagnostic procedure that is carried out to take a sample of a sample of a lump or abnormality in the body, including the breast. During the procedure, a thin needle is inserted into the target area. A syringe is then used to aspirate and remove small cells.
It is commonly used to evaluate breast lumps detected by physical examination or screening imaging tests such as mammography or ultrasound. The cells removed are examined under a microscope by a pathologist to determine whether they are cancerous (malignant) or non-cancerous (benign). A FNA biopsy is a quick and relatively painless procedure that can provide valuable information for diagnosing breast abnormalities with minimal scarring and recovery time. However, it may sometimes provide unclear results, requiring additional tests or a different biopsy technique for further evaluation.
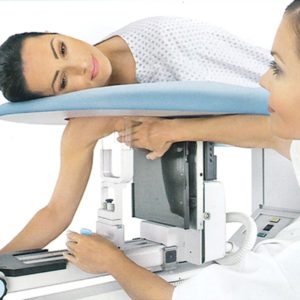
open (surgical) biopsy:
An open (surgical) biopsy is a procedure in which a doctor makes an incision to take a sample of tissue from a suspicious area for examination. Unlike minimally invasive techniques such as needle biopsies, an open biopsy is a surgical procedure and is usually performed under general anesthesia in an operating room. It’s frequently used when other biopsy methods, such as fine needle aspiration or core needle biopsy, are not helpful, or when a larger sample of tissue is needed for diagnosis. During the procedure, the surgeon removes a piece of the abnormal tissue or the entire lump. The sampled tissue is then sent to a pathologist for examination under a microscope to determine if it is cancerous (malignant) or non-cancerous (benign).
Vacuum-assisted core biopsy.
This procedure uses a vacuum-assisted device to remove multiple tissue samples through a single needle insertion. As compared to traditional core needle biopsy, where only one sample is taken per insertion, vacuum-assisted core biopsy allows multiple samples to be taken from different directions within the target area. This technique provides a more complete sample and increases the possibility of obtaining representative tissue, thereby improving diagnostic accuracy.
Vacuum-assisted core biopsy is generally performed under local anesthesia and can be done on an outpatient basis. It is commonly used to check for breast abnormalities detected by imaging tests such as mammography or ultrasound. The tissue samples collected are examined by a pathologist to determine if they are cancerous or benign, helping to support treatment decisions. In overall terms, a vacuum-assisted core biopsy is a safe and effective method for diagnosing breast abnormalities with minimal discomfort and scarring.
Before Breast Biopsy Test:
- A healthcare provider performs a physical examination of the breast to look for lumps, changes in shape, or other abnormalities.
- Mammograms, ultrasounds, MRIs, or other imaging tests may be done to visualize breast tissue and identify suspicious areas.
- The patient’s medical history is reviewed, including any previous breast conditions, family history of breast cancer, and other relevant details.
- The patient discusses any concerns, symptoms, or questions with the healthcare provider to determine the need for a biopsy and to understand the procedure.
- The patient gives informed consent after understanding the risks, benefits, and possible outcomes of the biopsy procedure.
After Breast Biopsy Test:
- The tissue samples taken during the biopsy are sent to a Pathologist who examines them under a microscope to determine whether the cells are cancerous or benign.
- The healthcare provider will tell the patient the biopsy results, explain whether the cells are malignant or benign, and discuss the next steps.
- If cancer cells are found, further tests may be needed to determine the stage and extent of the cancer. Treatment options such as surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or hormone therapy will be discussed and planned accordingly.
- Regardless of the biopsy results, the patient may need ongoing surveillance, follow-up appointments, or additional tests to ensure optimal breast health and to detect any changes or recurrence of abnormalities.
- Emotional support and counseling may be provided to the patient and her family to address any concerns, fears, or emotional reactions associated with the biopsy results and subsequent treatment decisions.
Conclusion:
In Conclusion, a breast biopsy is an important diagnostic procedure to investigate suspicious lumps or abnormalities in breast tissue. Various biopsy techniques are used, including core needle biopsy, fine needle aspiration biopsy, open (surgical) biopsy, and vacuum-assisted core biopsy, depending on the specific situation of the patient and the nature of the abnormality. A thorough clinical examination, imaging studies, patient history, and informed consent are essential steps before performing a biopsy. Neptune Diagnostics, located in Ghatkopar, offers advanced diagnostic services, including breast biopsies, to meet the community’s healthcare needs. After the biopsy, the tissue samples are examined by a pathologist to determine whether the cells are cancerous or benign, and the results are reported to the patient. Depending on the results of the biopsy, further tests and treatment planning may be needed. Emotional support and ongoing follow-up are also important parts of the post-biopsy care process. Overall, breast biopsy plays a role in diagnosing breast abnormalities and guiding appropriate treatment decisions to ensure optimal breast health. For more information on breast biopsy in Ghatkopar, please contact Neptune Diagnostics.